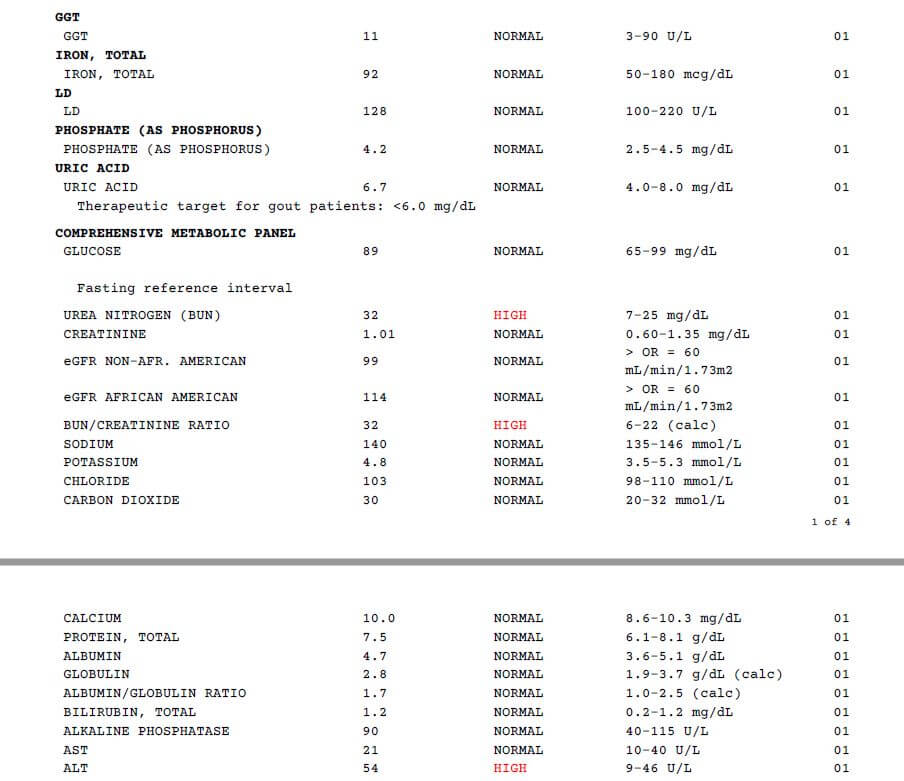
I had the blood work done for an upcoming physical this week. So, I was rattled and upset when I saw those unexpected numbers. In retrospect, I wish I had done that and will discuss this with him next week as an option. Interestingly, other markers look good. It explains how the tests are affected by your fat intake in the three days prior to testing. The same thing happened to me. I had always been an exerciser and healthy eater well, what I believed to be healthy eating but like you, that has shifted in the last year.
We try to clarify where these caveats are most important. Repeat every 6 months. To learn more about this approach and follow a simple keto meal plan, read through our guide to Mediterranean keto. Raising HDL artificially with drugs does not have the same benefit as raising it via a change in diet. This test is not available everywhere and may not be covered by insurance. Very-low Density Lipoprotein VLDL carries triglycerides and increased levels of it are strongly associated with greater cardiovascular risk. Although the evidence suggests that the keto diet can help optimize cholesterol in many groups of people, there are others that may not fare well, from a heart health perspective, when they eat a high fat, low carb diet. Central to regulating carbohydrates and fat metabolism in the body, insulin causes cells in the liver, muscle, and fat tissue to take up glucose from the blood. Within a couple of weeks to a month of keto dieting, you should be able to tell if your blood lipids are getting better or worse with a simple blood test and everything you learned throughout this article. This triggers an inflammatory response in which white blood cells called macrophages rush to eat up the LDL.
Editorial Open Access. Obes Control Ther 2 2 : As we all know, obesity is not only an aesthetic problem, but in developed countries, it is a disease that is reaching epidemic proportions and is associated with a multitude of medical conditions. Few examples of scientifically proven and its association with, are given below: 1. A lower life expectancy 2. A higher incidence with worse prognosis and evolution in different types of cancer such as the esophagus, stomach, colon, breast, endometrium, ovary, kidney and pancreas. Cardiovascular problems or diseases associated such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, phlebitis and venous thromboembolic disease. Endocrine problems where resistance to insulin, either directly or indirectly plays a key role, as the metabolic syndrome, impaired fasting glucose, carbohydrate intolerance, type 2 diabetes mellitus and polycystic ovary syndrome. Both male and female infertility and menstrual disorders 6. Orthopedic problems such as osteoarthritis.
